A fourth-year college student named Amanda walks into the laboratory and drops her backpack on a nearby chair. She has just finished her afternoon class on human resource management. The lab director, Dr Fred Travis, greets her and motions her to take a seat in front of the window. As they exchange small talk, Travis places a red cloth cap over the top of her head. It looks something like a ski cap, except for one thing―it has 32 sensors attached to it, connected to an electroencephalograph (EEG) machine that will measure the electrical activity of Amanda’s brain at 32 different points.
He monitors Amanda’s brainwave activity for the next few minutes to establish baseline readings. Then he asks Amanda to close her eyes and continue to sit quietly for a few more minutes. All the while wavy lines are moving across the computer screen, left to right.
Then he quietly instructs her to begin her practice of Transcendental Meditation―and in less than a minute, the waves change dramatically.
It’s clear to the naked eye, without analyzing the signals, that Amanda’s brain has shifted to a significantly more integrated, coherent style of functioning. That is, the different parts of her brain are communicating much more efficiently and effectively with each other.
Outwardly, Amanda appears simply to be sitting comfortably with her eyes closed. But inside, she is experiencing a fourth major state of consciousness.
Travis directs the Center for Brain, Consciousness, and Cognition at Maharishi International University (MIU) in Fairfield, Iowa, in the United States. He is one of the world’s leading scientists in the area of brain functioning and higher human development, with special focus on how the technique of Transcendental Meditation affects brain functioning and promotes personal growth.
Founded in 1971 by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, the noted Vedic scholar and scientist of consciousness, MIU is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission. It offers bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees in a wide range of subjects, from art to computer science, from creative writing to sustainable living, from regenerative organic agriculture to Ayurveda. Three quarters of its students come from outside the US, and the student body represents more than 80 countries.
All faculty, staff and students, as well as hundreds of members of the surrounding small-town community, practise the Transcendental Meditation technique. The technique, learned from a certified TM instructor, is a simple, natural, effortless procedure practised for 20 minutes twice each day while sitting comfortably with the eyes closed. It allows the mind to settle inward into a state of quiet―to “transcend,” or go beyond, the constant stream of thoughts and perceptions that fill the mind.
MIU has been a centre for research on Transcendental Meditation since its founding. Its first president, Robert Keith Wallace, conducted the first research on the technique while a PhD student at UCLA. Within two years, he had published his research in Science, Scientific American and the American Journal of Physiology.
His findings were striking. He found that during TM practice, as the mind settles inward, the body settles down into a uniquely deep state of rest, reflected in decreased heart rate, decreased respiration rate, and increased skin resistance. Yet the mind remains entirely awake―more awake than ever, in some respects―reflected in increased EEG alpha activity in the brain.
This combination of deep rest and heightened wakefulness had never been seen before in a laboratory. Wallace described it as a “wakeful hypometabolic state”―“restful alertness,” in simpler English―and he declared it to be a fourth state of consciousness beyond the three familiar states of waking, dreaming, and sleeping.
Wallace was studying the classic state of samadhi, known in the Upanishads as turiya, “the fourth,” and termed Transcendental Consciousness by Maharishi.
This exalted state had been known and celebrated for millennia, in India and in traditions around the world. But Wallace was uncovering the constellation of changes that occur in body during this restfully alert experience―its “neurophysiological correlates.”
The TM technique does not involve focusing or concentrating the mind or attending to one’s thoughts or one’s breathing. It is not “mindfulness.” One does not try to control one’s body’s functions, as in biofeedback. The technique is effortless.
One student describes her experience during TM practice in this way: “I have the experience of transcending all activity and experiencing awareness as an unbounded unity. There is no longer any sense of ‘me’ and ‘not me,’ no longer any thought or feelings or even a body, just the Self, and that is all there is, and that is all I am.”
Yet this simple and natural experience of transcending leads to a host of physiological changes, all in the direction of rest, repair, and balance.
Wallace’s publications sparked a wave of research on the TM technique that has continued to this day. To date, research has been conducted at more than 250 universities and research institutes around the world, and studies have been published in more than 170 journals in a range of fields.
These studies have further detailed the striking physiological changes that take place during the technique. They have also looked at the long-term effects, where the findings have been equally remarkable. These include improved health, increased intelligence (IQ) and creativity, increased self-esteem and self-actualisation, and improved interpersonal relationships.
Many of these findings are notable because they had also never been seen before in modern science. For example, intelligence and creativity grow through childhood but level off in adolescence. Yet with TM practice, these values resume growing regardless of age. TM practice “unfreezes” their growth.
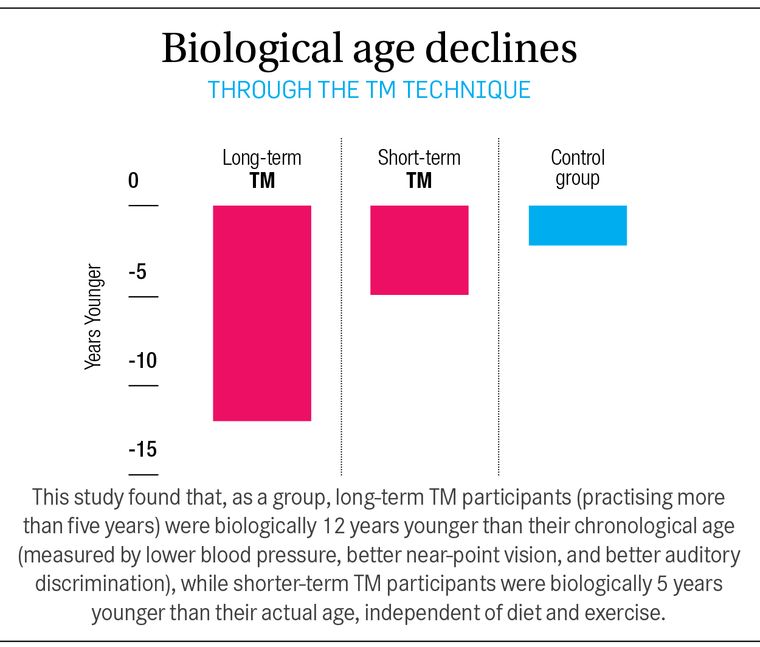
Wallace predicted that, given the TM technique’s ability to dissolve stress, it may affect the rate at which the body ages. Physiologists distinguish between our chronological age (our age in years) and our “biological age”―the age of the body as determined by a cluster of measures.
Wallace found that people who had been meditating more than five years were biologically 12 years younger than their chronological age. Several other studies found that TM practice can extend lifespan by 23%.
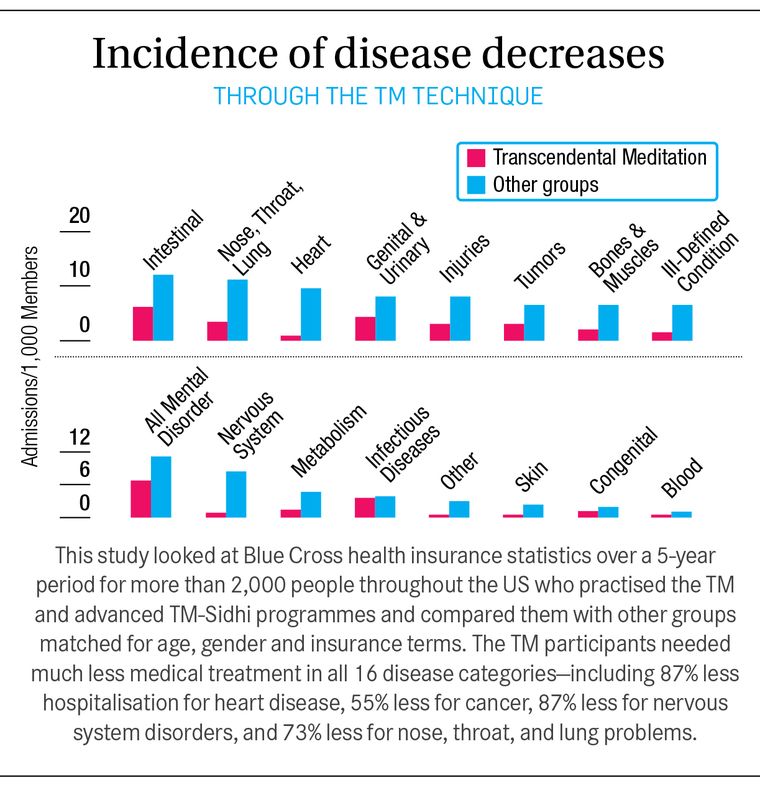
One of the most dramatic findings emerged from health insurance statistics. David Orme-Johnson, then chair of MIU’s psychology department, tracked 2,000 people over a five-year period across the US who practised the TM technique.
The data was collected by Blue Cross, the health insurer. The statistics for the meditation group were compared with those of a control group selected by the insurance company to match the TM group for age, gender, education, profession and insurance terms.
The result: The TM group went to hospital 56% less often for illness or surgery. The differences between the TM group and the control group were significant in all age groups but most conspicuous in older groups. The TM group also required 50% fewer doctors’ visits. The TM meditators had not become disenchanted with doctors―for maternity, they used health care just as much as the control group.
Starting in 1990, research on cardiovascular health became a major focus at MIU. Over the following years, the US government’s National Institutes of Health (NIH) invested more than $25 million dollars in MIU’s research on TM and cardiovascular health. With this support, MIU professor Robert Schneider and his colleagues, in partnership with universities around the US, conducted a series of studies that made headlines worldwide.
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, according to the World Health Organization, accounting for 32% of all global deaths. Yet modern medicine has failed to cure or even curb this disease or even pinpoint the cause. It has only identified the risk factors.
This is why Schneider’s studies were so newsworthy. He and his teams found that TM practice shows great promise for preventing and even curing cardiovascular disease.
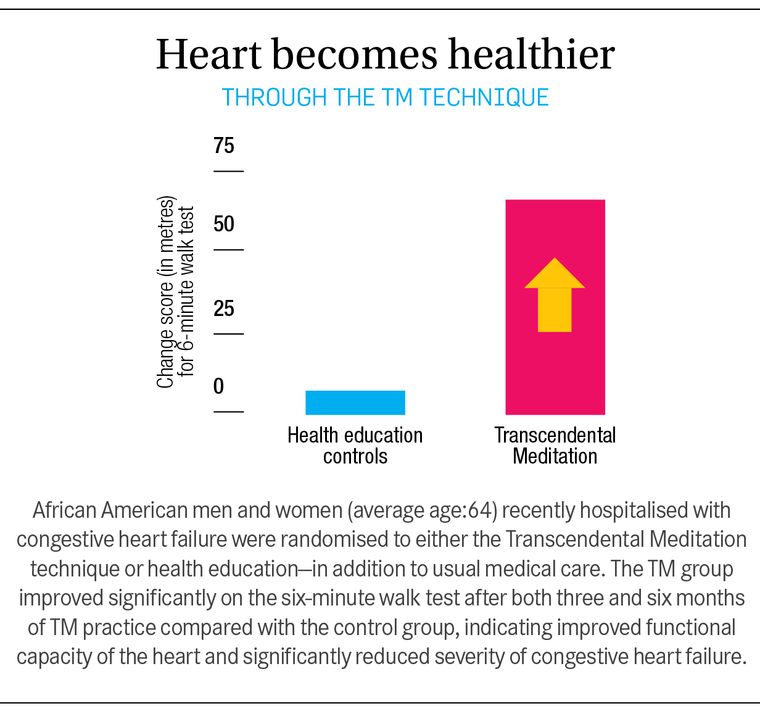
They focused first on hypertension, a leading risk factor for heart disease. They tested the TM programme on elderly African Americans, who have 50% more hypertension than white Americans, twice the level of cardiovascular disease, and a far higher rate of deaths from it. This is because they’re subject to higher chronic socio-environmental stress.
But when they learned the TM technique, their blood pressure dropped significantly, as much as with standard drug treatments―but with no side effects, with higher patient compliance, and at far lower cost. The meditating group also lived longer. Compared with the control group, those in the TM group were 23% less likely to die from any cause, 30% less likely to die from heart disease, and 49% less likely to die from cancer.
In these studies, the subjects made no changes in their diets or exercise habits. The effects were solely due to the regular experience of transcending using the TM technique.
Studies found that TM practice reduces other leading risk factors for heart disease, including cholesterol and free radicals, smoking and alcohol abuse, and psychological and socio-environmental stress.
Prevention is the best medicine, but for those who already have heart disease, Schneider and company also found that TM practice can actually reverse its damaging effects. TM practice unclogs arteries and reverses atherosclerosis. It reverses enlargement of the heart (left-ventricular hypertrophy). The practice even reduces the severity of congestive heart failure―and heart failure is the end result of all heart diseases. Again, subjects in these studies made no other changes in their lifestyle beyond their TM practice.
Turning their attention to another global epidemic, Schneider and company found that TM practice significantly reduces the risk of diabetes. One study found that after just 16 weeks of TM practice, patients with both heart disease and type 2 diabetes not only had lower blood pressure, but had also significantly better blood glucose and insulin levels―signifying reduced insulin resistance and more stable functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
“This research shows that the Transcendental Meditation technique helps the body tap into its inner intelligence and normalise function,” Schneider said. “These subjects simply transcended regularly, and their cardiovascular and endocrine systems regained more perfect balance.”
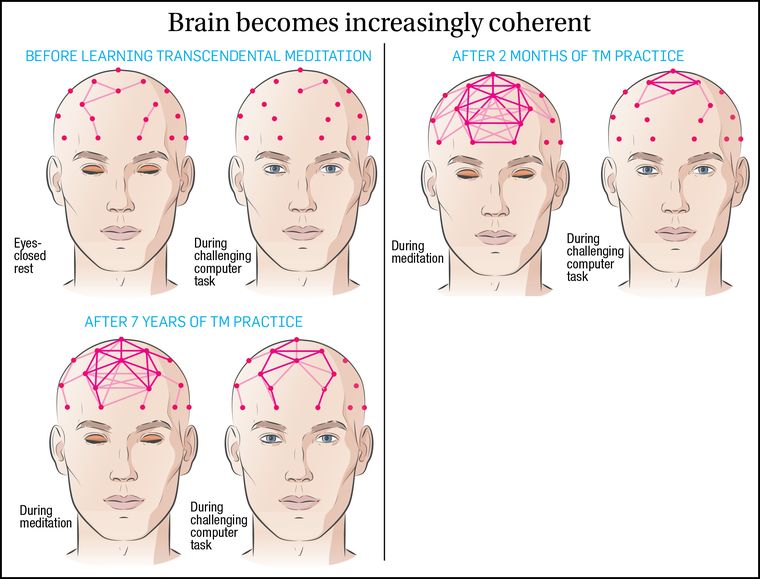
Travis has most recently been looking at how the integrated brain functioning characteristic of TM practice increasingly persists even outside of meditation―over time it becomes the brain’s normal style of functioning.
The computer-generated drawings (above) illustrate alpha-range EEG coherence and how it increases during TM practice―and then increasingly becomes the brain’s normal style of functioning even outside of meditation.
The lighter lines show coherence (communication) between the two linked brain areas of about 70%, the heavier lines coherence of 80% or higher (100% is perfect coherence). The more effectively the various brain areas communicate, the better the brain performs.
“These are really remarkable findings,” Travis said. “Before we started researching the Transcendental Meditation technique, we had no idea that the brain could function with this exceptional level of integration. And now we’ve learned that we can cultivate the brain to function in this way all the time.”
This is also remarkable, because the higher one’s level of brainwave coherence, the greater one’s intelligence, creativity, moral maturity, learning ability, and many other positive values, according to research studies at MIU and elsewhere.
MIU students have the option of receiving a Brain Integration Progress Report. Students have their brainwave coherence measured shortly after they enroll and then again shortly before they graduate, to see how much their brain integration has increased during their years at MIU.
“This is a remarkable contribution to education,” Travis says. “And any school, college or university can implement this same approach and give their students these same benefits, without any changes to their curriculum apart from setting aside two short periods for Transcendental Meditation practice.”
Travis is often asked whether other meditation techniques produce these same results.
“Different meditation techniques involve different mental procedures,” Travis explains, “and therefore they produce different modes of brain functioning.
For example, meditation techniques that involve focusing or concentrating the mind―known as focused attention techniques―produce beta/gamma activity in the brain, typical of any active mental processing.
A second category of techniques, called open monitoring, includes mindfulness procedures, which involve monitoring aspects of one’s experience―one’s thoughts, breathing, sensory perceptions, physical sensations―without evaluating them. These procedures induce theta activity in the brain, seen when people reflect on mental concepts.
The third category, which includes the Transcendental Meditation technique, is called automatic self-transcending. It involves procedures that transcend their own activity, enabling the mind to go beyond (transcend) the meditation process and into the experience of pure consciousness. These techniques elicit frontal alpha-1 coherence, indicating the brain’s executive control centre is functioning in an integrated manner.
“All meditation techniques are not the same,” Travis says. “Other procedures have their value. But so far only the TM technique has been shown to produce this integrated and coherent style of brain functioning along with the wide-ranging constellation of benefits that studies have found.”
Over the past 40 years the technique has been applied in a variety of practical fields, where it has been studied by MIU scientists and others.
In schools, when students and faculty learn the practice, IQ and creativity increase, students’ grades increase, graduation rates increase, and overall school climate improves.
Also read
- Exclusive: 'Yoga a proven way to enhance human potential', President Murmu to THE WEEK
- Yoga asanas meet medicine: What medical research at AIIMS, Delhi, shows
- 'Sperm count and motility skyrocketed after attending yoga classes in AIIMS': Raja Singh
- 'Yoga an excellent method to deal with lifestyle diseases: Cardiologist Gautam Sharma
- 'Yoga can prevent onset of disease': Dr Rima Dada of AIIMS
- 'Yoga is a perennial gift of Indian wisdom to the world': Union Minister Sarbananda Sonowal
In companies, when managers and employees learn the TM technique, stress declines, illness and absenteeism decline, cooperation increases, productivity increases, and the companies become more profitable.
In prisons, when inmates learn the technique, they sleep better, their health improves, they commit fewer infractions, and most important, they return to prison at a far lower rate than non-meditating prisoners.
Among veterans suffering from PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder), when they start TM practice, their symptoms decrease markedly, and they reintegrate into their families and the workplace more quickly and easily.
How can such a simple technique produce such a wide constellation of benefits―for cognitive development, for health, for personality growth and interpersonal relationships?
“It’s all about the experience of transcending,” Travis said. “The experience is simple, natural, and incredibly profound. It dissolves stress and resets and rebalances the whole mind-body system. Maharishi likens it to watering the root of a tree, where a single act nourishes the tree’s countless leaves and branches. ‘Water the root to enjoy the fruit,’ he said. Consciousness is the most fundamental value of life, and now we know we can cultivate and improve our lives from that deepest level.”
Craig Pearson, PhD, has served as executive vice president and vice president of academic affairs at Maharishi International University and is currently special assistant to the president. He is the author of The Supreme Awakening: Experiences of Enlightenment Throughout Time ― And How You Can Cultivate Them. He would like to thank David and Arlene Leffler and Fred Travis.